Saint Kitts is an island nation in the Caribbean that has a rich and vibrant history, culture, and society. From its vibrant and colourful festivals to its diverse cuisine, Saint Kitts offers something for everyone. Its heritage has been shaped by the various cultures that have settled on the island over the years. In this blog post, we will explore the history and culture of Saint Kitts, and examine how they have shaped the island’s modern-day society. Saint Kitts is a small Caribbean island located in the Leeward Islands chain of the West Indies. Over the centuries, this tropical paradise has served as home to a variety of different cultures and societies, including indigenous peoples, British colonizers, and African slaves. Each of these groups has left their mark on the island, creating a unique and fascinating history that is still alive today. In this blog post, we will explore the history, culture, and society of Saint Kitts in order to gain a better understanding of its rich heritage.
Pre-Colonial Saint Kitts
Before the arrival of Europeans, Saint Kitts was populated by the Carib and Arawak people. These indigenous people had their own distinct culture and language, with some elements of their culture still present in the modern day.
For hundreds of years, the Carib and Arawak people were the dominant inhabitants of the island. They hunted and fished for food, and traded with other Caribbean cultures. They also built stone walls around villages and cultivated land to grow maize, sweet potatoes, and other crops.
The Carib and Arawak people had a complex social structure, with clear roles and responsibilities within the community. Men were typically hunters and fishermen while women took care of the household duties. The Caribs believed in a variety of gods who controlled their daily lives and activities. This religious system was rooted in their spiritual beliefs.
In 1493, Christopher Columbus visited Saint Kitts as part of his voyage to discover new lands. His arrival marked the start of a long period of European domination that would have a lasting impact on the island’s culture and society.
The British Period
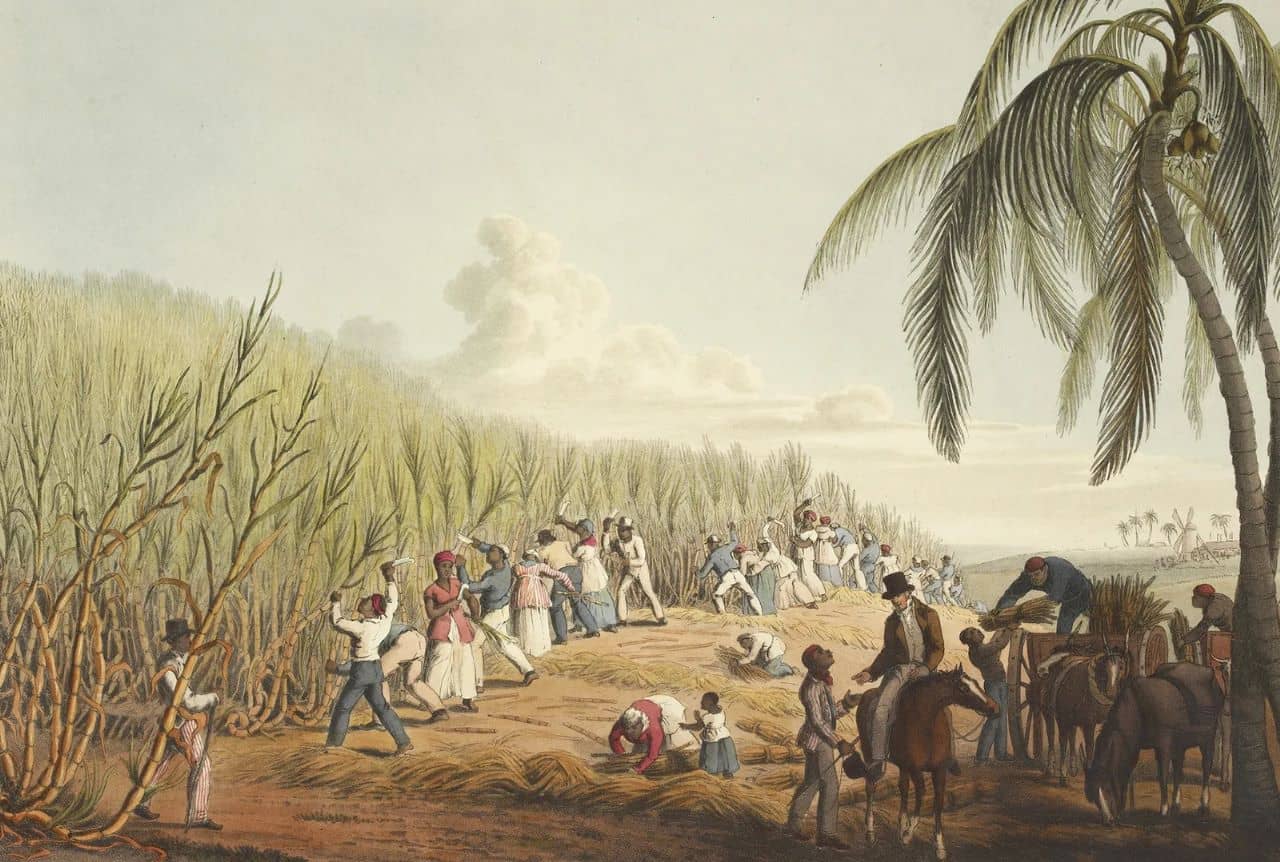

The British Period in Saint Kitts began in 1623 when a group of British settlers arrived on the island, establishing the first English colony in the Caribbean. In 1493, history was made when Christopher Columbus first laid eyes on the islands during his epic voyages. Then, 30 years later, the English made their grand entrance to the islands, led by Thomas Warner, who chose to settle on the west coast of St Kitts after forming an agreement with the Carib chief, Ouboutou Tegremante. Not long after, in 1625, the French also arrived and decided to share the island with their English counterparts, ultimately splitting it into two sections. Soon after, the English began colonizing the nearby island of Nevis in 1628.
During this period, Saint Kitts became an important military outpost for the British Navy and saw the establishment of several key naval bases. This allowed the British to maintain a strong presence in the region and secure their strategic interests. As the sugar industry flourished and grew, so did the population of Saint Kitts.
The island also experienced an influx of Europeans, particularly Irish settlers, who established small farms and businesses on the island. The Irish influence is still seen today in the language, culture, and cuisine of Saint Kitts.
The British Period saw the expansion of Christianity throughout Saint Kitts, with churches and missionary schools being built. Education also expanded during this time, with many government-funded schools being constructed. This period of growth and prosperity ultimately came to an end when Britain abolished slavery in 1834.
Post-Independence
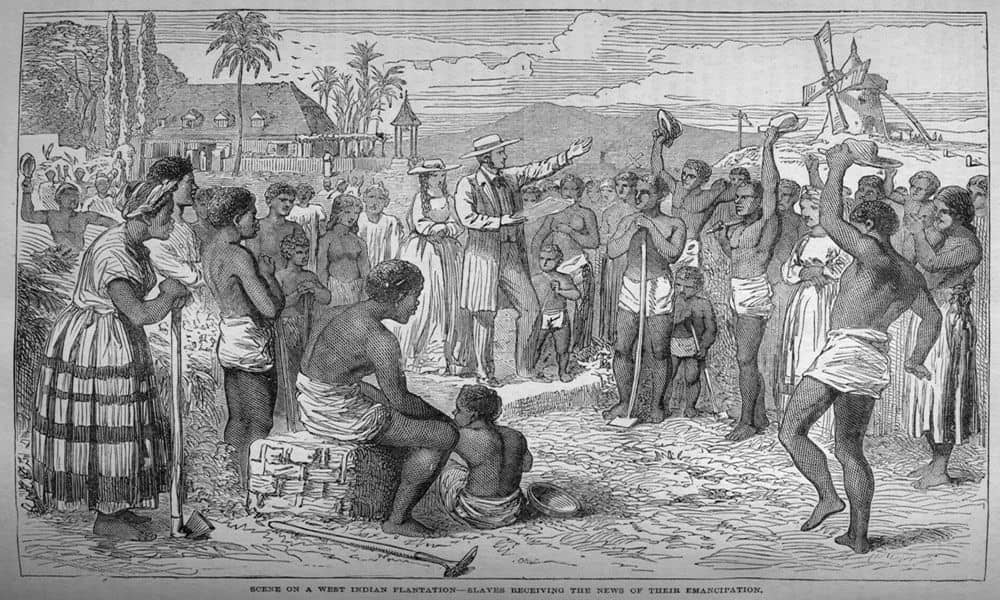

The Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis gained full independence from the United Kingdom in 1983. Since then, the two islands have been governed by a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary democracy. The economy of Saint Kitts and Nevis is based mainly on tourism, hotels, and small-scale manufacturing.
Since independence, the government of Saint Kitts and Nevis has pursued a number of policies to promote economic growth and development. Tourism has become an important part of the island’s economy, with the number of visitors increasing each year. This has created numerous jobs in the hospitality and service industry, helping to improve the standard of living for many people on the islands.
The government has also been involved in several initiatives to preserve Saint Kitts’ cultural heritage. These include the creation of national parks, the protection of historic sites, and the promotion of traditional arts and crafts.
The culture of Saint Kitts and Nevis is a unique blend of African, Caribbean, and European influences. The people of the islands are proud of their rich cultural heritage and take great pride in preserving it. Music, dance, and storytelling continue to be an important part of life on Saint Kitts and Nevis, ensuring that its history and traditions remain alive for generations to come.